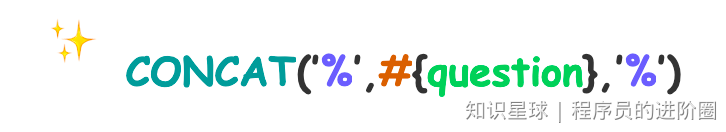Mybatis 那点破事.md 23 KB
title: 第九篇:Mybatis ! ORM,动态SQL、动态代理
Mybatis 那点破事! ORM,动态SQL、动态代理
作者:Tom哥
公众号:微观技术
博客:https://offercome.cn
人生理念:知道的越多,不知道的越多,努力去学
什么是 MyBatis?
答案:
Mybatis 是一个半 ORM(对象关系映射)框架,它内部封装了 JDBC,开发时只需要关注 SQL 语句本身,不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement 等繁杂的过程。程序员直接编写原生态 sql,可以严格控制 sql 执行性能,灵活度高。
MyBatis 可以使用 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将 POJO 映射成数据库中的记录,避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。
通过 xml 文件或注解的方式将要执行的各种 statement 配置起来,并通过 java 对象和 statement 中 sql 的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的 sql 语句,最后由 mybatis 框架执行 sql 并将结果映射为 java 对象并返回。(从执行 sql 到返 回 result 的过程)。
MyBatis 优点?
答案
- 基于 SQL 语句编程,相当灵活,不会对应用程序或者数据库的现有设计造成任何影响,SQL 写在 XML 里,解除 sql 与程序代码的耦合,便于统一管理;提供 XML 标签,支持编写动态 SQL 语句,并可重用。
- 与 JDBC 相比,减少了 50%以上的代码量,消除了 JDBC 大量冗余的代码,不需要手动开关连接;
- 很好的与各种数据库兼容(因为 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 来连接数据库,所以只要 JDBC 支持的数据库 MyBatis 都支持)。
- 能够与 Spring 很好的集成;
- 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的 ORM 字段关系映射;提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组件维护。
MyBatis 缺点?
答案:
- SQL语句的编写工作量较大,尤其当字段多、关联表多时,对开发人员编写SQL语句的功底有一定要求。
- SQL语句依赖于数据库,导致数据库移植性差,不能随意更换数据库
ORM 是什么?
答案:
ORM(Object Relational Mapping),对象关系映射。
是一种为了解决关系型数据库数据与简单Java对象(POJO)的映射关系的技术。简单来说,ORM是通过使用描述对象和数据库之间映射的元数据,将程序中的对象自动持久化到关系型数据库中。
为什么说 Mybatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
答案:
- Hibernate属于全自动ORM映射工具,使用Hibernate查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取,所以它是全自动的。
- 而Mybatis在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写SQL来完成,所以,被称之为半自动ORM映射工具。
JDBC 编程有哪些不足之处?
答案:
- 1、数据连接创建、释放频繁造成系统资源浪费从而影响系统性能
- 解决:在mybatis-config.xml中配置数据链接池,使用连接池统一管理数据库连接。
- 2、sql语句写在代码中造成代码不易维护
- 解决:将sql语句配置在XXXXmapper.xml文件中与java代码分离。
- 3、向sql语句传参数麻烦,因为sql语句的where条件不一定,可能多也可能少,占位符需要和参数一一对应。
- 解决:Mybatis自动将java对象映射至sql语句。
- 4、对结果集解析麻烦,sql变化导致解析代码变化,且解析前需要遍历,如果能将数据库记录封装成pojo对象解析比较方便。
- 解决:Mybatis自动将sql执行结果映射至java对象。
MyBatis 和 Hibernate 有什么区别?
答案:
1、相同点
- 都是对jdbc的封装,都是应用于持久层的框架。
2、不同点
- 映射关系
- MyBatis 是一个半自动映射的框架,配置Java对象与sql语句执行结果的对应关系,多表关联关系配置简单
- Hibernate 是一个全表映射的框架,配置Java对象与数据库表的对应关系,多表关联关系配置复杂
- SQL优化和移植性
- Hibernate 对SQL语句封装,提供了日志、缓存、级联(级联比 MyBatis 强大)等特性,此外还提供 HQL(Hibernate Query Language)操作数据库,数据库无关性支持好,但会多消耗性能。如果项目需要支持多种数据库,代码开发量少,但SQL语句优化困难。
- MyBatis 需要手动编写 SQL,支持动态 SQL、处理列表、动态生成表名、支持存储过程。开发工作量相对大些。直接使用SQL语句操作数据库,不支持数据库无关性,但sql语句优化容易。
MyBatis 的使用过程?
答案:
1、 创建 SqlSessionFactory。可以从配置或者直接编码来创建SqlSessionFactory
StrinString resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
2、 通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession,SqlSession(会话)可以理解为程序和数据库之间的桥梁
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
3、 通过sqlsession执行数据库操作
可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句:
Blog blog = (Blog)session.selectOne("org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper.selectBlog", 101);更常用的方式是先获取Mapper(映射),然后再执行SQL语句:
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); Blog blog = mapper.selectBlog(101);
4、 调用session.commit()提交事务。如果是更新、删除语句,我们还需要提交一下事务。
5、 调用session.close()关闭会话
MyBatis 生命周期?
答案:
上面提到了几个MyBatis的组件,一般说的MyBatis生命周期就是这些组件的生命周期。
1、SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了。因此 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 实例的生命周期只存在于方法的内部。
2、SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory 是用来创建SqlSession的,相当于一个数据库连接池,每次创建SqlSessionFactory都会使用数据库资源,多次创建和销毁是对资源的浪费。所以SqlSessionFactory是应用级的生命周期,而且应该是单例的。
3、SqlSession
SqlSession相当于JDBC中的Connection,SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的生命周期是一次请求或一个方法。
4、Mapper
映射器是一些绑定SQL语句的接口。映射器接口的实例是从 SqlSession 中获得的,它的生命周期在sqlsession事务方法之内,一般会控制在方法级。
🚄 MyBatis通常也是和Spring集成使用,Spring可以帮助我们创建线程安全的、基于事务的 SqlSession 和映射器,并将它们直接注入到我们的 bean 中,我们不需要关心它们的创建过程和生命周期
模糊查询 like 语句该怎么写?
答案:
1 、’%${question}%’ 可能引起SQL注入,不推荐
2 、"%"#{question}"%" ,因为#{…}解析成sql语句时候,会在变量外侧自动添加单引号’ ',所以这里 % 需要使用双引号" ",不能使用单引号 ’ ',不然会查不到任何结果。
3 、CONCAT(’%’,#{question},’%’) 使用CONCAT()函数(推荐)
是否支持延迟加载?
答案:
1、Mybatis支持association关联对象和collection关联集合对象的延迟加载,association指的就是一对一,collection指的就是一对多查询。在Mybatis配置文件中,可以配置是否启用延迟加载lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false。
2、它的原理是,使用CGLIB创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器 invoke() 方法发现 a.getB() 是null值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联B对象的sql,把B查询上来,然后调用a.setB(b),于是a的对象b属性就有值了,接着完成a.getB().getName()方法的调用。这就是延迟加载的基本原理。
3、当然了,不光是Mybatis,几乎所有的包括Hibernate,支持延迟加载的原理都是一样的。
如何获取自动生成的主键值?
答案:
新增标签中添加:keyProperty=" ID " 即可
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="userId" > insert into user( user_name, user_password, create_time) values(#{userName}, #{userPassword} , #{createTime, jdbcType= TIMESTAMP}) </insert>这时候就可以完成回填主键
mapper.insert(user); user.getId;
支持动态 SQL 吗?
答案:
Mybatis 动态 sql 可以在 Xml 映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态 sql,执行原理 是根据表达式的值 完成逻辑判断并动态拼接 sql 的功能。
Mybatis 提供了 9 种动态 sql 标签:trim 、 where 、 set 、foreach 、if 、 choose 、 when 、 otherwise 、 bind
1、if,根据条件来组成where子句
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</if>
</select>
2、choose (when, otherwise),和Java 中的 switch 语句有点像
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
</when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
3、foreach,用来循环的,可以对集合进行遍历
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
<where>
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="ID in (" separator="," close=")" nullable="true">
#{item}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
Xml 映射文件中有哪些标签?
答案:
除了常见的**select | insert | update | delete 标签之外,还有 ** <resultMap>、<parameterMap>、<sql>、<include>、<selectKey>,加上动态 sql 的 9 个标签
不同xml映射文件id是否可以重复?
答案:
不同的xml映射文件,如果配置了 namespace,那么id可以重复;如果没有配置 namespace,那么id不能重复。
原因 namespace+id 作为Map<String,MapperStatement>的key使用,如果没有namespace,就剩下id,那么id重复会导致数据互相覆盖。有了namespace,自然id就可以重复,namespace不同,namespace+id自然也不同。
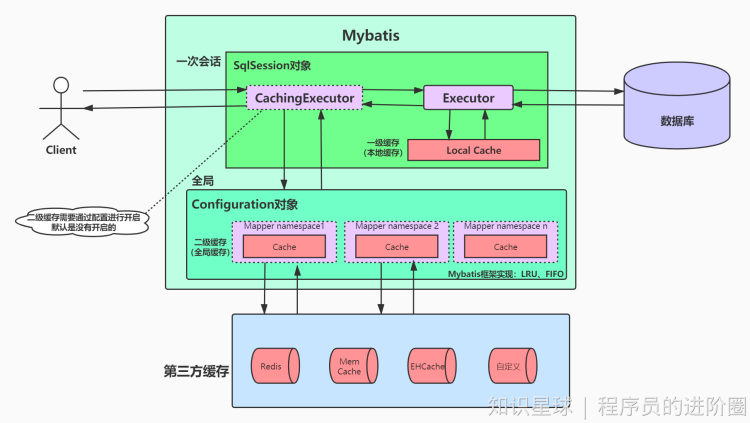
Mybatis 的一级、二级缓存?
答案
Mybatis 里面设计了两级缓存来提升数据的检索效率,避免每次数据访问都去查询数据库。
1、一级缓存: 基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,各个SqlSession之间的缓存相互隔离。当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该 Session 中的所有 Cache 就 将清空,默认打开一级缓存。
2、二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap 存储,不同之处在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),可以在多个SqlSession之间共享,并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache。默认不打开二级缓存,要开启二级缓存,使用二级缓存属性类需要实现Serializable序列化接口(可用来保存对象的状态),可在它的映射文件中配置。
3、对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存 Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了 C/U/D 操作后,默认该作用域下所有 select 中的缓存将被 clear。
MyBatis的工作原理?
答案:
- 读取 MyBatis 配置文件——mybatis-config.xml 、加载映射文件——映射文件即 SQL 映射文件,文件中配置了操作数据库的 SQL 语句。最后生成一个配置对象。
- 构造会话工厂:通过 MyBatis 的环境等配置信息构建会话工厂 SqlSessionFactory。
- 创建会话对象:由会话工厂创建 SqlSession 对象,该对象中包含了执行 SQL 语句的所有方法。
- Executor 执行器:MyBatis 底层定义了一个 Executor 接口来操作数据库,它将根据 SqlSession 传递的参数动态地生成需要执行的 SQL 语句,同时负责查询缓存的维护。
- StatementHandler:数据库会话器,串联起参数映射的处理和运行结果映射的处理。
- 参数处理:对输入参数的类型进行处理,并预编译。
- 结果处理:对返回结果的类型进行处理,根据对象映射规则,返回相应的对象。
为什么 Mapper 接口不需要实现类?
答案:
主要是借助于 动态代理来实现。我们来看一下获取Mapper的过程:
定义的Mapper接口没有实现类,Mapper 映射其实是通过动态代理实现的。七拐八绕地进去看一下,发现获取Mapper的过程,首先获取Mapper代理工厂 MapperProxyFactory
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } else { try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception var5) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5); } } }public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; …… protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache); return this.newInstance(mapperProxy); } }通过Proxy.newProxyInstance 为 Mapper接口创建一个 动态代理对象 MapperProxy,所有的方法维护在一个 Map methodCache 集合中
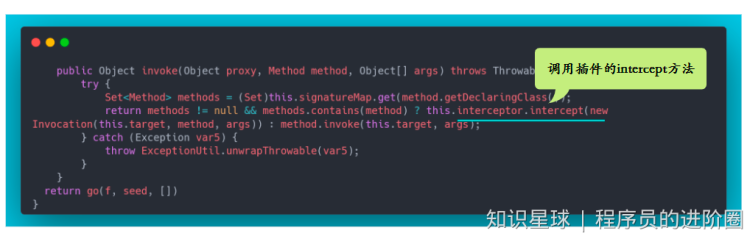
当我们对 Mapper接口 某个方法(如:queryUserById)调用时候,触发动态代理 的 invoke 方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } if (this.isDefaultMethod(method)) { return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable var5) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5); } MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args); }MapperMethod里的excute方法,真正去执行sql。其实绕一圈,最终是通过SqlSession的实例去运行对象的sql。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object param; Object result; switch(this.command.getType()) { case INSERT: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case UPDATE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case DELETE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case SELECT: if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) { this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (this.method.returnsMany()) { result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsMap()) { result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) { result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param); } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; 。。。。省略 } }- SimpleExecutor:每执行一次update或select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象。
- ReuseExecutor:执行update或select,以sql作为key查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭Statement对象,而是放置于Map内,供下一次使用。简言之,就是重复使用Statement对象。
- BatchExecutor:执行update(没有select,JDBC批处理不支持select),将所有sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理。与JDBC批处理相同。
- 实现Mybatis的Interceptor接口并重写intercept()方法
这里我们只是在目标对象执行目标方法的前后进行了打印;
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor { Properties props=null; @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("before……"); //如果当前代理的是一个非代理对象,那么就会调用真实拦截对象的方法 // 如果不是它就会调用下个插件代理对象的invoke方法 Object obj=invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("after……"); return obj; } }然后再给插件编写注解,确定要拦截的对象,要拦截的方法
@Intercepts({@Signature( type = Executor.class, //确定要拦截的对象 method = "update", //确定要拦截的方法 args = {MappedStatement.class,Object.class} //拦截方法的参数 )}) public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor { Properties props=null; @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("before……"); //如果当前代理的是一个非代理对象,那么就会调用真实拦截对象的方法 // 如果不是它就会调用下个插件代理对象的invoke方法 Object obj=invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("after……"); return obj; } }最后,在 MyBatis配置文件里面配置插件
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="xxx.MyPlugin"> <property name="dbType",value="mysql"/> </plugin> </plugins>- Mapper 接口方法名和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的 id 相同;
- Mapper 接口方法的输入参数类型和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的 parameterType 的类型相同;
- Mapper 接口方法的输出参数类型和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的 resultType 的类型相同;
- Mapper.xml 文件中的 namespace 即是 mapper 接口的类路径。
Mybatis 都有哪些 Executor 执行器?
答案:
Mybatis有三种基本的Executor执行器,SimpleExecutor、ReuseExecutor、BatchExecutor。
Mybatis 插件运行原理?
答案:
Mybatis 可以编写针对 ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler、Executor 4个接口的插件,插件的原理就是在这四大对象调度的时候,插入一些我我们自己的代码。
Mybatis 使用JDK的动态代理,为目标对象生成代理对象。它提供了一个工具类Plugin,实现了InvocationHandler接口。
使用Plugin生成代理对象,代理对象在调用方法的时候,就会进入invoke方法,在invoke方法中,如果存在签名的拦截方法,插件的intercept方法就会在这里被我们调用,然后就返回结果。如果不存在签名方法,那么将直接反射调用我们要执行的方法。
如何编写一个插件?
答案:
我们自己编写MyBatis 插件,只需要实现拦截器接口 Interceptor (org.apache.ibatis. plugin Interceptor ),在实现类中对拦截对象和方法进行处理。
MyBatis 如何进行分页?
答案:
Mybatis使用RowBounds对象进行分页,它是针对ResultSet结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页,可以在sql内直接书写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能,也可以使用分页插件来完成物理分页。
分页插件的原理是什么?
答案:
分页插件的基本原理是使用Mybatis提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的sql,然后重写sql,根据dialect方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数。
Mybatis 的 Xml 映射文件中,不同的 Xml 映射文件,id 是否可以重复?
答案:
不同的 Xml 映射文件,如果配置了 namespace,那么 id 可以重复;如果没有配置 namespace,那么 id 不能重复;
原因就是 namespace+id 作为 Map的 key使用的,如果没有 namespace,就剩下 id,那么,id 重复会导致数据互相覆盖。有了 namespace,自然 id 就可以重复,namespace 不同,namespace+id 自然也就不同。
Mapper 接口调用时有哪些要求?
答案:
Mybatis 引入哪些设计模式?
答案:
1、Builder模式
如:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、XMLConfigBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder、XMLStatementBuilder、CacheBuilder
2、工厂模式
如:SqlSessionFactory、ObjectFactory、MapperProxyFactory
3、单例模式
如:ErrorContext和LogFactory
4、代理模式
Mybatis实现的核心,比如 MapperProxy、ConnectionLogger,用的jdk的动态代理;还有executor.loader包使用了cglib或者javassist达到延迟加载的效果;
5、组合模式
如:SqlNode和各个子类ChooseSqlNode等
6、模板模式
如:BaseExecutor和SimpleExecutor,还有BaseTypeHandler和所有的子类例如IntegerTypeHandler
7、适配器模式
如:Log的Mybatis接口和它对jdbc、log4j等各种日志框架的适配实现
8、装饰者模式
如:Cache包中的cache.decorators子包中等各个装饰者的实现
9、迭代器模式
如:迭代器模式PropertyTokenizer